does the excavator of the mason compact the soil Understanding the whys and hows of soil compaction can help you make efficient equipment choices. With an operating weight of 4.2 tonnes, the Bobcat® 335 compact excavator is ideal for general excavation work, digging for founda-tions, demolition work, lifting jobs and much more. Thanks to ideal weight distribution, the 335 offers exceptional stability in all operating conditions. Like all Bobcat® compact excava-
0 · Two Common Compaction Mistakes, and How to Avoid Them
1 · The Science of Soil Compaction
2 · The Constructor
3 · Soil Compaction: Methods, Meaning, and Effects
4 · Soil Compaction Handbook
5 · SOIL COMPACTION AND STABILITY
6 · Restoration Techniques
7 · Fundamentals of Soil Compaction
8 · Factors Affecting Compaction of Soil and their Effect on Different
9 · Effective Depth of Soil Compaction
10 · 15.3: Relieving and Preventing Compaction
Just one of these brands (let’s pick Bobcat as an example) “offers 13 different compact excavators in its lineup, and those machines range in class size from 1 to 8 metric tons — with zero, reduced and conventional tail swing options,” explains Kyle Emanuel, product information specialist at Bobcat Co.
Understanding the whys and hows of soil compaction can help you make efficient equipment choices.Learn the basics of soil compaction and stability, including soil classifications, Proctor tests, and soil saturation levels. See charts and examples of cohesive and cohesionless soils, and how . Learn how to avoid over compaction and under compaction of sand and other soil types with the right equipment and methods. This blog explains the effects of compaction on .Learn how water content, amount of compaction, type of soil and method of soil compaction influence the dry density and optimum water content of soil. See compaction curves and .
Learn how to improve soil health and permeability for riparian restoration projects. Find out how to test, decompact, and amend soil using various tools and methods.
Learn about soil compaction, its types, methods, and effects on soil types and construction projects. Find out how to identify and classify soil, and how to achieve optimal density and .Learn how soil compaction is achieved by applying mechanical energy to reduce voids ratio and increase shear strength. Find out the factors affecting compaction, such as water content, soil . Learn how to relieve and prevent compaction in soils, a common soil degradation problem. Find out the causes, effects, and solutions of compaction, and how to measure and manage soil compaction.
This report evaluates the effectiveness of different lift thicknesses for soil compaction in embankment construction. It suggests that 0.30 meters (12 inches) for coarse-grained soils .
Understanding the whys and hows of soil compaction can help you make efficient equipment choices.Learn the basics of soil compaction and stability, including soil classifications, Proctor tests, and soil saturation levels. See charts and examples of cohesive and cohesionless soils, and how to deal with unstable subgrades. Learn how to avoid over compaction and under compaction of sand and other soil types with the right equipment and methods. This blog explains the effects of compaction on soil strength, stability and structure, and provides some guidelines and tricks for beginners. Learn how soil compaction is the practice of applying mechanical effort to densify soil by reducing void space between particles. Find out the factors that affect soil compaction, such as soil type, moisture content, and compaction equipment.
Learn how water content, amount of compaction, type of soil and method of soil compaction influence the dry density and optimum water content of soil. See compaction curves and examples for different soil types.Learn how to improve soil health and permeability for riparian restoration projects. Find out how to test, decompact, and amend soil using various tools and methods.Learn about soil compaction, its types, methods, and effects on soil types and construction projects. Find out how to identify and classify soil, and how to achieve optimal density and moisture content.Learn how soil compaction is achieved by applying mechanical energy to reduce voids ratio and increase shear strength. Find out the factors affecting compaction, such as water content, soil type and compactive effort, and how to perform and interpret laboratory compaction tests.
Learn how to relieve and prevent compaction in soils, a common soil degradation problem. Find out the causes, effects, and solutions of compaction, and how to measure and manage soil compaction.
Two Common Compaction Mistakes, and How to Avoid Them
The Science of Soil Compaction

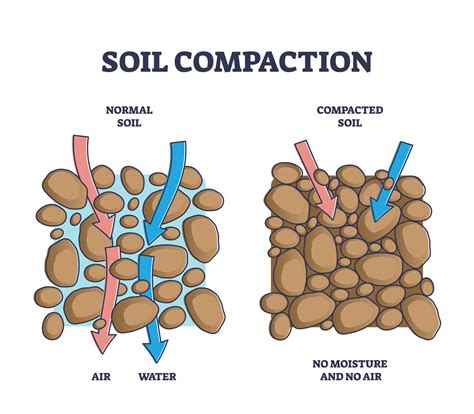
This report evaluates the effectiveness of different lift thicknesses for soil compaction in embankment construction. It suggests that 0.30 meters (12 inches) for coarse-grained soils and 0.20 meters (8 inches) for fine-grained soils could be .
Understanding the whys and hows of soil compaction can help you make efficient equipment choices.
Learn the basics of soil compaction and stability, including soil classifications, Proctor tests, and soil saturation levels. See charts and examples of cohesive and cohesionless soils, and how to deal with unstable subgrades.
Learn how to avoid over compaction and under compaction of sand and other soil types with the right equipment and methods. This blog explains the effects of compaction on soil strength, stability and structure, and provides some guidelines and tricks for beginners.
Learn how soil compaction is the practice of applying mechanical effort to densify soil by reducing void space between particles. Find out the factors that affect soil compaction, such as soil type, moisture content, and compaction equipment.Learn how water content, amount of compaction, type of soil and method of soil compaction influence the dry density and optimum water content of soil. See compaction curves and examples for different soil types.Learn how to improve soil health and permeability for riparian restoration projects. Find out how to test, decompact, and amend soil using various tools and methods.Learn about soil compaction, its types, methods, and effects on soil types and construction projects. Find out how to identify and classify soil, and how to achieve optimal density and moisture content.
Learn how soil compaction is achieved by applying mechanical energy to reduce voids ratio and increase shear strength. Find out the factors affecting compaction, such as water content, soil type and compactive effort, and how to perform and interpret laboratory compaction tests. Learn how to relieve and prevent compaction in soils, a common soil degradation problem. Find out the causes, effects, and solutions of compaction, and how to measure and manage soil compaction.

The Constructor
Soil Compaction: Methods, Meaning, and Effects
E85 Key Specifications. E85 Bobcat Compact Excavator (Tier 4) Operating Weight. 18,960 lb. Bucket Digging Force. 14,509 lbf. Maximum Reach at Ground Level. 286.8 in.
does the excavator of the mason compact the soil|Soil Compaction Handbook